
Spinach is believed to be of Persian origin, and arrived on European shores around the 11th Century. The chlorophyll packed leaf belongs to the chenopodiaceae family which includes nutritional powerhouses including beets, Swiss chard and Quinoa.
Spinach is available all year round, but in season during spring. The leaf is known to help restore energy, increase vitality and improve the quality of blood.
The rich dark green leaves indicate that the spinach is rich in chlorophyll, which has been linked to natural cancer prevention by blocking carcinogenic effects within the body, whilst protecting DNA from damage.
Spinach is rich in glycoglycerolipid molecules which have been found to be beneficial in protecting the lining of the digestive tract from damage. It has been shown to be the leading vegetable in showing significant protection against aggressive prostate cancer.
Epoxyxanthophylls are found in plentiful supply within spinach, and much like other better known carotenoids it has excellent anti-cancer properties.
Spinach is rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin K, A, Manganese and folate, and if that is not enough it is a concentrated form of health promoting phytonutrients and flavonoids.
The health benefits of spinach include anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer, these benefits are mainly due to the rich array of flavonoids and carotinoids.
Spinach is a rich source of antioxidants, this means that it can lower our risk of health problems related to oxidative stress. There is also a link with the daily consumption of spinach and the prevention of eye problems, including age related macular degeneration.
Spinach is an excellent food source for bone health due to its rich vitamin K content, as well as calcium and magnesium. The vitamin K helps to prevent the break down of bone and plays a vital role in strengthening bone mass.
What is the nutrient content of spinach?
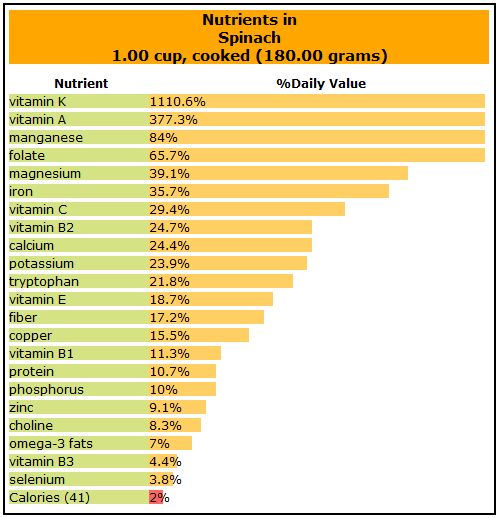
A closer look at the benefits of some of the vitamins and minerals found in spinach.
Vitamin K
- Promotes normal healthy clotting
- Prevents heart disease and arteral calcification
- Improves vascular health, leading to fewer varicose veins
- Maintains healthy bones
- Acts as an adjunct to vitamin D
- Helps to reduce the risk of developing prostrate cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer and leukaemia
Vitamin A
- Maintains normal skin function
- Maintains a healthy vision
- Promotes a healthy fuctioning immune system
- Maintains neurological function
- Reduces inflammation, through fighting free radical damage
Manganese - Mineral
- Supports the formation of healthy bones through absorption of calcium
- Supports collagen production
- Helps with blood sugar control
- Contributes to the prevention of oxygen related damage and damage from ultra violet (UV) light
- Antioxidant, fights free radical damage. Diets low in manganese have been linked to skin problems and asthma
- Proper functioning of the thyroid gland
- Promotes metabolism of fats and carbohydrates
Folate - Vitamin
- Promotes brain development and improves functioning
- Promotes a health nervous system
- Decreases risk of various cancers, including breast cancer
- Supports a healthy cardiovascular system
- Helps nervous system development in the fetus
- Assists in the production of red blood cells
- May reduce the risk of depression
Magnesium - Mineral
- Helps protein synthesis
- Supports the nervous system
- Improves cellular metabolism
- Regulates hearth rhythm
- Reduces the risk of osteoporosis
- Reduces eclamptic seizures
- Helps with muscle relaxation
- Assists with bone and teeth formation
- Regulates the body's use of calcium and other minerals
- Helps maintain structural health of cell membranes
- Reduces the risk of type two diabetes
- Reduces the symptoms of asthma
Iron - Mineral
- Formation of red blood cells
- Supports healthy muscle function
- Helps in brain development
- Helps to regulate body temperature
- Supports a healthy neurological system
- Oxygen carrier from one cell to another.
Vitamin C
- Supports the immune system
- Increases iron absorption
- Protects cells from oxidating damage
- Helps reduce the risk of heart disease, including coronary heart disease and stroke
- Helps in the formation of collagen, carnitine, and catecholemines.


 Articles by subject
Articles by subject Recent Articles
Recent Articles





